What is wet brain?
Wet brain is a term that is used to describe a medical condition known as Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome.
What is Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?

Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome is a brain disorder which is caused by a deficiency of the Vitamin known as Thiamine. Vitamin B 1. It usually happens in people with heavy and long-term alcohol abuse. It can also happen in other conditions which leads to loss of Vitamin B1.
What is the difference between Wernicke’s encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome?
Wernicke’s encephalopathy is an acute and short-term problem. It may lead to a more chronic phase of the brain disorder known as Korsakoff syndrome.
Is Korsakoff progressive?
Korsakoff as mentioned before is a brain disorder due to excessive alcohol intake and depletion of Vitamin B 1. If a person continues to consume alcohol it is likely that the disorder will progress. However, if one stops alcohol and eats well and takes care of the nutrition then the progress can be stopped.
What vitamin is implicated in Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?
A type of B vitamin known as Vitamin B1 or thiamine is implicated in the development of Wernicke’s Korsakoff Syndrome. Vitamin B1 is essential to convert the food into energy and provide the energy to the brain for optimum functioning. Since Vitamin B1 is not produced in the body, the only source is through food and adequate nutrition.
Why do people who abuse alcohol have Vitamin B1 deficiency?

People who intake alcohol heavily over a long period of time will lead to inadequate absorption of vitamins and minerals. Additionally, they may neglect their nutrition. The cells also will have an impaired ability to process these vitamins.
What happens to the brain of someone who abuses alcohol over a long period of time?
Alcohol affects the brain as it is a toxin. It affects the brain both in the short term and the long term. Alcohol as soon as one drinks and gets intoxicated people start losing their judgement and focus. Sometimes people may have accidents following alcohol intoxication which may result in head injury and brain damage.
What are the symptoms of Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?

Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome is a type of brain damage which occurs due to Vitamin B1 deficiency. Wernicke’s encephalopathy is the condition which occurs first and is acute. If this is treated well then Korsakoff syndrome may not develop. The symptoms of Wernicke’s encephalopathy include being confused, having unstable gait and some vision problems.
Sometimes especially if untreated, Wernicke’s encephalopathy may lead to a more chronic and permanent form of brain damage known as Korsakoff syndrome. This is characterized by memory loss especially short-term memory loss and creating false memories (known as confabulation).
How long does it take to develop Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?
People with chronic alcohol intake will develop this slowly whereas in certain surgeries such as Bariatric surgery where part of the stomach may be removed, this develops in a matter of weeks.
Why do people who abuse alcohol get Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?

People who abuse alcohol heavily suffer from nutritional deficiency especially Vitamin B1. This could be more in the developing world. 90% of Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome occurs due to alcohol abuse over long term. Usually this is precipitated by infections.
In what other conditions do people get Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?
Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome also occurs in other conditions that lead to Vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency. This includes cancers, people who have had gastric bypass, eating disorders leading to malnourishment and kidney dialysis.
What is the age of onset of Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?
The age of onset of Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome is usually 30 years onwards.
How is Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome is mainly by detailed history, clinical and physical examination.
What are the scan and blood results like in Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?
There is no diagnostic blood tests or scans for diagnosing Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome. However you doctor may order an array of tests to rule out other conditions and to check electrolyte imbalance, liver damage, brain damage etc.
It Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome reversible?

In the early stages, Wernicke’s encephalopathy is reversible. In later stages it will potentially lead to the irreversible form of Korsakoff syndrome.
What is the treatment for Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?
Treatment for Wernicke’s encephalopathy is usually high dose Vitamin B1 (thiamine) given through the veins and supportive treatment till recovery occurs.
How long can you live with Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome?
This is varied and usually when Korsakoff syndrome sets in, prognosis is only for a matter of months or few years.
Is Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome the same as alcohol dementia?
Alcohol dementia is a term used to denote Wernicke’s Korsakoff syndrome.
Is it OK to take thiamine every day?
Yes, it is safe to take the Vitamin Thiamine on an everyday basis.
How long should I take thiamine?
If you have been admitted and treated for Wernicke’s encephalopathy then oral thiamine (Vitamin B1) should be taken at a dose of 250 mg once a day for as long as you consume alcohol or even indefinitely.
What food are high in thiamine?

Outer shell of rice is high in thiamine. That is why highly polished rice can lead to Thiamine deficiency. Eggs and fish are high in Thiamine. Nuts and seeds are a good source too. Seafood, meat, nuts and eggs are all good sources of thiamine.
Do eggs contain thiamine?
Eggs are a good source of Vitamin B1 (thiamine). They are a cheap source of thiamine and is readily available. It is part of balanced diet and very important in alcohol rehabilitation.
What dosage of thiamine should I take?
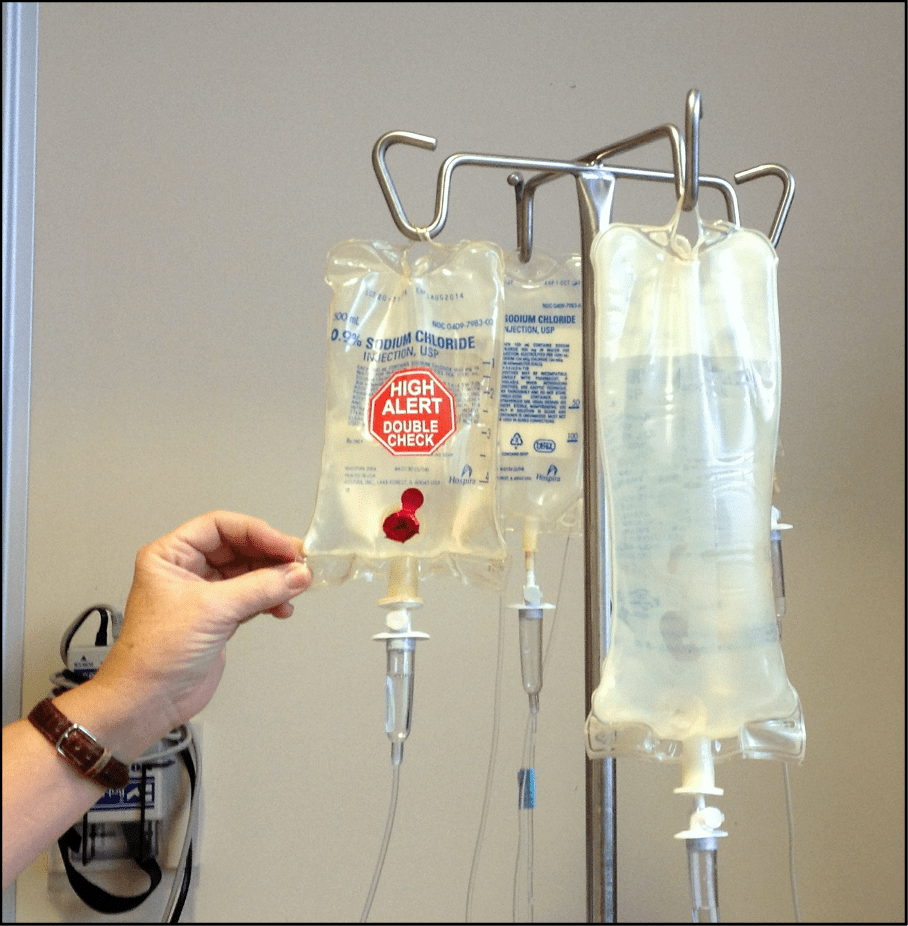
In mild Vitamin B1 deficiency people are advised to take around 25 mg of Vitamin B1. In more moderate cases of deficiency higher doses may be required 250 mg per day. When people present with Wernicke’s encephalopathy 500 mg intravenously is given 3 times a day for 3 days. Then 250 mg per day intravenously for the rest of the week. Leading website design company in Coimbatore. This is usually followed by 100 mg intravenously till patient recovers and takes adequate nutrition and oral supplements. Vitamin B1 intravenous is given before glucose is administered to prevent cell damage and death.
What are the symptoms of low thiamine?
Low Thiamine (Vitamin B1 deficiency) leads to a condition known as beri beri. This can cause weakness of muscles and loss of reflexes. It can cause pain and irritability. Fatigue, loss of appetite and tingling sensation in the limbs can also occur.









